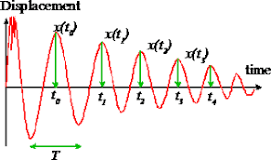
In the context of mechanical systems, a damped vibration is a vibration that decreases in amplitude over time. This can occur due to various factors such as friction, air resistance, or the presence of a damper. The energy of the vibration is dissipated as the vibration dies out, rather than being transferred to other parts of the system.
There are two main types of damped vibrations: underdamped and overdamped. In an underdamped vibration, the amplitude of the vibration decreases over time, but the system does not return to its equilibrium position. In an overdamped vibration, the system returns to its equilibrium position more quickly, but with less oscillation.
Also read: Troubleshooting comcast email common
Damped vibrations are important to consider in the design of mechanical systems, as they can affect the performance and durability of the system. In some cases, it may be desirable to reduce the damping in a system to increase its performance, while in other cases it may be necessary to increase the damping to reduce the risk of damage or wear
Other forms of energy generated by vibration.
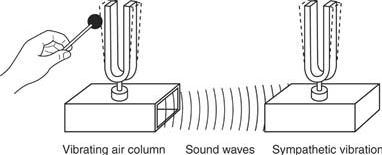
One form of energy that can be generated by vibration is mechanical energy. This type of energy is associated with the movement or displacement of physical objects, such as when a vibrating tuning fork sets a membrane into motion, or when the vibrations of a drumhead are transmitted to the air as sound waves.
Another form of energy that can be generated by vibration is electrical energy. This can occur when certain materials, such as piezoelectric crystals, are subjected to mechanical stress or strain. The vibration of these materials can cause them to produce an electric current, which can then be harnessed and used as a source of power.
There are also other forms of energy that can be generated by vibration, such as thermal energy (which is produced as a result of the friction between moving parts), and radiant energy (which is emitted as electromagnetic waves).
Kinetic energy: Vibrating objects can also generate kinetic energy, which is the energy of motion. For example, when a person walks or runs, the vibrations caused by their footsteps can be converted into electricity by piezoelectric generators, which are devices that produce an electric current when subjected to mechanical stress.
Magnetic energy: Some devices, such as linear motors, use vibration to generate a magnetic field, which can then be used to produce electricity. Linear motors work by vibrating a series of magnets back and forth within a coil of wire, which generates an alternating current.
Gravitational energy: Some researchers are exploring the use of vibration to harness gravitational energy. For example, a device called a gravitator uses vibration to cause a small object to oscillate back and forth, generating a small amount of gravitational energy in the process.
Vibrational energy: Vibrational energy is the energy associated with the vibrational motion of atoms and molecules within a substance. This type of energy can be harnessed and converted into electricity using a variety of techniques, including the use of piezoelectric materials and thermoelectric generators.
Acoustic energy: Sound waves are a form of vibration, and they can be used to generate energy through a process called acoustic energy harvesting. This technique involves using sensors to convert the energy of sound waves into an electrical current. One example of a device that uses this technique is an "acoustic flashlight," which uses the energy of clapping to power a small LED light.
Wind energy: Vibration can also be used to generate wind energy. For example, some wind turbines use a system of gears and bearings to convert the rotational motion of the turbine into vibration, which is then used to generate electricity.
Tidal energy: The movement of water caused by tides is another example of vibration that can be used to generate energy. Tidal energy can be harnessed through the use of tidal turbines, which are similar to wind turbines, but which are placed in bodies of water and use the movement of tides to generate electricity.
Seismic energy: The vibrations caused by earthquakes and other seismic activity can also be harnessed and converted into electricity. One example of a device that uses this technique is a seismic harvester, which is a type of generator that is placed underground and uses the energy of vibrations caused by earthquakes and other seismic events to produce electricity.




0 Comments